Scanning Electron Microscope – Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS)
By Allschoolabs
• Published on August 2, 2025
2 views
Category: Analytical
- Last updated: August 2, 2025
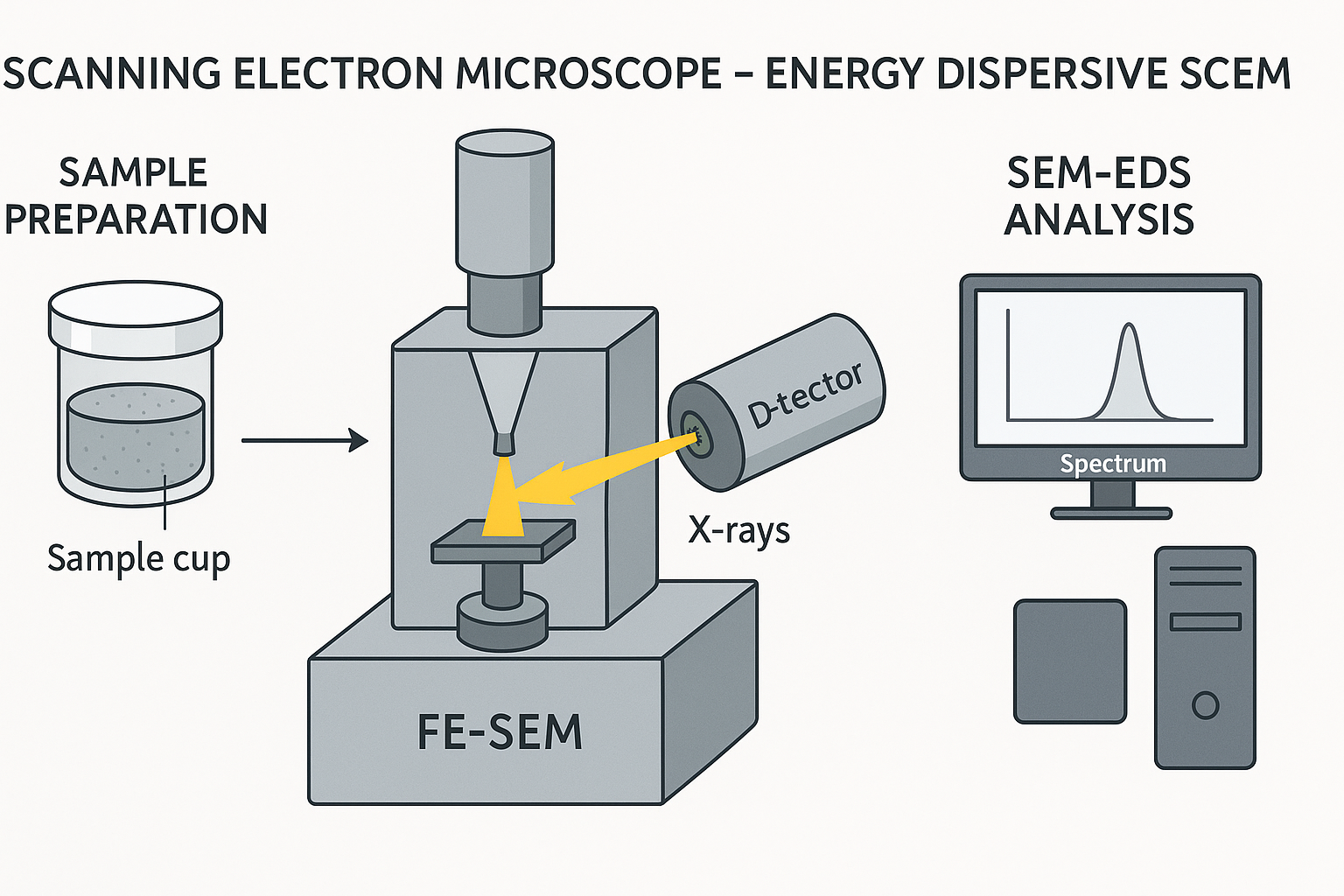
The Scanning Electron Microscope energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) Phenom Prox model, manufactured by phenomWorld Eindhoven, Netherlands was used to carry out the morphology analysis. Sample is placed on the Aluminium holder stub using sticky carbon tape. The sample was insulated using gold and then grounded electrically. The samples each are then labeled on their stub, then dried in the oven at 60oC. Nitrogen line was opened at 50 psi and the vent button is pressed to fill the area with nitrogen for proper purging of the chamber. The sample holder stub was then placed in the sample chamber holes and the door was shut and the rotary pump picked and a vacuum of 5 x 10-5 Pa was created. The filament light was switched on and the monitor too automatically switched on. At this stage, the accelerator voltage was 15kV and the filament burned out. The atoms on the surface are excited by the electron beam, emitting specific wavelengths of X-rays that are characteristic of the atomic structure of the elements. An energy dispersive detector (a solid-state device that discriminates among X-ray energies) can analyze these X-ray emissions. Appropriate elements are assigned, yielding the composition of the atoms on the specimen surface. The lowest scan mode of 10x is picked and the TV scan clicked. The magnification is then taking to 1000x at a slow scan, 2000, 3000 to 5,000. The Energy dispersion spectrum scan on the intensity of each of the element present and gives the molar concentration in %, then Image was saved. This procedure is called The Scanning Electron Microscope Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) and is useful for analyzing the composition of the surface of a specimen